Research
Publications
Computer Vision
[2013] Fusing Visual and Tactile Sensing for Manipulation of Unknown Objects
In the Proceedings of ICRA Mobile Manipulation Workshop on Interactive Perception
[2013] 3D Object Reconstruction with a Single RGB-Depth Image
In the Proceedings of Proceedings of VISAP
- Abstract: This paper presents a fast method for acquiring 3D models of unknown objects lying on a table, using a single viewpoint. The proposed algorithm is able to reconstruct a full model using a single RGB + Depth image, such as those provided by available low-cost range cameras. It estimates the hidden parts by exploiting the geometrical properties of everyday objects, and combines depth and color information for a better segmentation of the object of interest. A quantitative evaluation on a set of 12 common objects shows that our approach is not only simple and effective, but also the reconstructed model is accurate enough for tasks such as robotic grasping.
[2012] A-Contrario Detection of Aerial Target Using a Time-of-Flight Camera
In the Proceedings of the SSPD (Sensor Signal Processing for Defence
- Abstract: Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras provide 3D pointcloud data in real time, even in case of changing illumination conditions. Thanks to their advantages in comparison to classic vision techniques, ToF devices have been already used in several application fields but their suitability in aerial scenarios is still under study. Thus, this paper presents the evaluation of a new approach for detecting an aerial target within the working range of the used ToF camera, defining a boom-and-receptacle refueling system as the context of this work. The detection method is based on a-contrario easoning, using the 3D point-cloud data acquired by a PMD Cam Cube 3.0: the sky is presented as noise in the range images, thus the target is perceived as a deviation from a model of complete randomness. In order to obtain a decision criterion, a study based on mean and variance analysis has been carried out. The results on real images show that the detection is performed successfully with the proposed approach, showing its robustness with respect to the number of false alarms.
[2012] Object Pose Estimation and Tracking by Fusing Visual and Tactile Information
In the Proceedings of MFI (Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems)
[2012] Object Modeling and Detection
Book Chapter In Hacking the Kinect by Jeff Kramer, Nicolas Burrus, Daniel Herrera C., Florian Echtler and Matt Parker (Apress, 2012)
[2011] Textureless Object Recognition and Arm Planning for a Mobile Manipulator
In the Proceedings of the 53rd International Symposium ELMAR-2011, IEEE.
- Abstract: Manipulator robots require of comprehensible perception systems that permit them to interact with the environment, localize target objects and perform complex manipulation tasks. To do that, a full-step manipulation process has to be performed involving recognition of supporting planes, object clustering, its recognition and finally smooth arm trajectory planning with obstacle avoidance. The goal of this paper is to propose a general and practical strategy for designing a 3D perception system architecture that can robustly plan for the location of texture and untextured objects for the purpose of grasping. Our proposed system includes RGB-D calibrated system to acquire 3D color scenario data, a 7-DOF arm controlled with a PMAC 2-PCI and a precise arm-end grasp. A validation of the overall proposed idea with some experimental results and a comparison of the benefits with similar initiatives is presented.
[2011] Object reconstruction and recognition leveraging an RGB-D camera
In the Proceedings of the 12th IAPR Conference on Machine Vision Applications
- Abstract: Recently, sensing devices capable of delivering real-time color and depth information have become available. We show how they can benefit to 3D object model acquisition, detection and pose estimation in the context of robotic manipulation. On the modeling side, we propose a volume carving algorithm capable of reconstructing rough 3D shape with a low processing cost. On the detection side, we find that little robustness can be directly added to classical feature-based techniques, but we propose an interesting combination with traditionally less robust techniques such as histogram comparison. We finally observe that 3D pose estimates can also be greatly improved using the depth measurements.
[2010] Robust Pedestrian Detection using a Time-Of-Flight Camera
Talk at the 8th Robocity2030 Workshop, Madrid, Spain
[2010] 3D Object Model Acquisition and Recognition with a Time-of-Flight camera
Talk at the 7th Robocity2030 Workshop, Madrid, Spain
[2009] Monocular human upper body pose estimation for sign language analysis 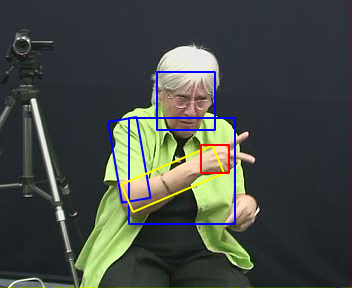
Talk at the 4th Multitel Spring Workshop, Mons, Belgium
- PDF (presentation)
- Abstract: We present a system to track human upper body using a single camera. The goal is to extract relevant features for sign language recognition, such as location, velocity and configuration of forearms and hands. Motion blur, rapid moves, self-occlusions and non-rigid deformations make the independent tracking of individual part difficult, ambiguous and not very reliable. Thus, we experiment top-down approaches based on pictorial models which aim at simultaneously modeling the geometry of human parts, the appearance of each part and the temporal continuity in a unified statistical framework. First results will be shown on the NGT corpus of Dutch sign language videos.
[2009] Image segmentation by a contrario simulation 
Pattern Recognition journal
- PDF (preprint)
- Abstract: Segmenting an image into homogeneous regions generally involves a decision criterion to establish whether two adjacent regions are similar. Decisions should be adaptive to get robust and accurate segmentation algorithms, avoid hazardous \textit{a priori} and have a clear interpretation. We propose a decision process based on \textit{a contrario} reasoning: two regions are meaningfully different if the probability of observing such a difference in pure noise is very low. Since the existing analytical methods are intractable in our case, we extend them to allow a mixed use of analytical computations and Monte-Carlo simulations. The resulting decision criterion is tested experimentally through a simple merging algorithm, which can be used as a post-filtering and validation step for existing segmentation methods.
[2008] Bottom-up and top-down object matching using asynchronous agents and a contrario principles
In the Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Vision Systems (ICVS’08)
- Link at Liris
- Abstract: We experiment a vision architecture for object matching based on a hierarchy of independent agents running asynchronously in parallel. Agents communicate through bidirectional signals, enabling the mix of top-down and bottom-up influences. Following the so-called a contrario principle, each signal is given a strength according to the statistical relevance of its associated visual data. By handling most important signals first, the system focuses on most promising hypotheses and provides relevant results as soon as possible. Compared to an equivalent feed-forward and sequential algorithm, our architecture is shown capable of handling more visual data and thus reach higher detection rates in less time.
[2008] Segmentation d’image par simulations a contrario (fr)
In the Proceedings of RFIA 2008
- Link at Liris
- Abstract: Segmenting an image into homogeneous regions generally involves a decision criterion to establish whether two adjacent regions are similar. Decisions should be adaptive to get robust and accurate segmentation algorithms, avoid hazardous a priori and have clear justification. We propose a decision process based on an a contrario reasoning: two regions are meaningfully different if the probability of observing such a difference in pure noise is very low. Since the existing analytical methods are intractable in that case, we generalize them to allow a mixed use of analytical computations and Monte-Carlo simulations. The resulting decision criterion is tested experimentally through a simple merging algorithm, which can be used as a post-filtering and validation step for existing segmentation methods.
[2006] Smart retina as a contour-based visual interface 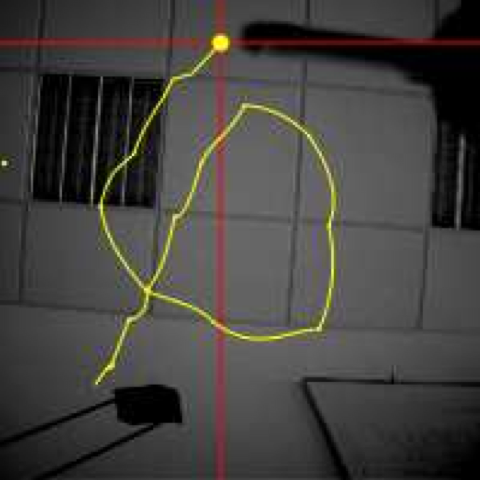
In the Proceedings of Distributed Smart Cameras Workshop (DSC’06), 2006
- Abstract: The purpose of this work is to provide a robust vision-based input device. In our system, a programmable retina is looking at the user who sends commands by moving his hand. The fusion between the acquisition and the processing functions of the retina allows a close adaptation to the lighting conditions and to the dynamic range of the scene. Thanks to its optical input and massive parallelism, the retina computes efficiently the contours of the moving objects. This feature has nice properties in terms of motion detection capabilities and allows a dramatic reduction in the volume of data to be output of the retina. An external low-power processor then performs global computations on the output data, such as extreme points or geometric moments, which are temporally filtered to generate a command.
[2006] Adaptive Vision Leveraging Digital Retinas: Extracting Meaningful Segments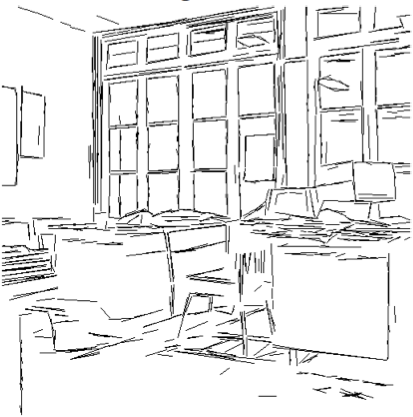 
In the Proceedings of Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems International Conference (ACIVS’06), 2006
- Slides of the oral presentation: PDF
- Abstract: In general, the less probable an event, the more attention we pay to it. Likewise, considering visual perception, it is interesting to regard important image features as those that most depart from randomness. This statistical approach has recently led to the development of adaptive and parameterless algorithms for image analysis. However, they require computer-intensive statistical measurements. Digital retinas, with their massively parallel and collective computing capababilities, seem adapted to such computational tasks. These principles and opportunities are investigated here through a case study: extracting meaningful segments from an image.
[2005] Détection de segments significatifs sur rétine artificielle programmable (fr)
Rapport de stage de master
- Résumé: Ce travail se place à l’intersection de deux approches à priori indépendantes du traitement des images : une approche matérielle et algorithmique basée sur l’architecture cellulaire massivement parallèle des rétines ar tificielles ; et une approche a contrario statistiquement fondée de la perception cherchant à minimiser le nombre de paramètres nécessaires pour analyser les images. Nous nous proposons d’étudier la combinaison de ces deux univers à travers un opérateur simple et générique : l’extraction de segments significatifs.
[2004] Visualization and White Matter Fiber Tracking with Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Images 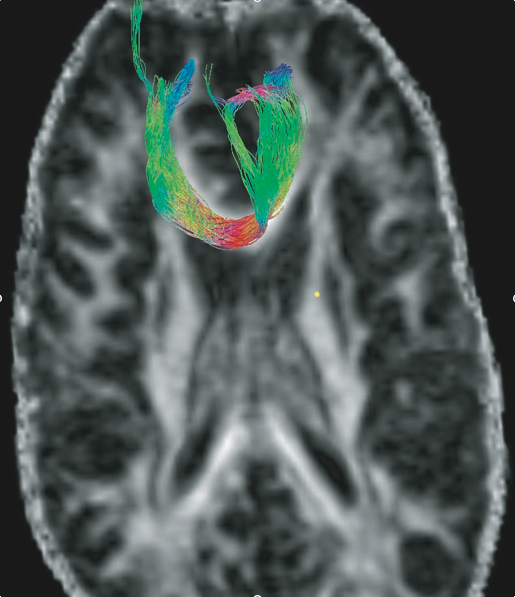
Internship report, Siemens Corporate Research (Princeton)
- Abstract: We propose to model DT-MRI fiber tracking using particle filters. The resulting algorithm can handle both noise and ambiguities raised by partial volume effects and crossing fibers. Combined with a simple clustering algorithm, distinct fiber branches can be explored without loss of tracking power. Interesting results were obtained with a reasonable computation time. Last, the flexibility of the framework makes it possible to add many parameters to the model, opening good perspectives for future improvements.
- Patent application #20060229856 class: 703011000 (USPTO)
C++ related
[2004] Introduction to C++ metaprogramming
Tutorial
- Abstract: This report aims at simplifying the discovery of the static C++ world. Mostly relying on Todd Veldhuisen Techniques for scientific C++ and Andrei Alexandrescu Modern C++ Design, we try to give to the novice metaprogrammer most of the basics notions he should learn, in a didactic way. The goal is also to make the reader work and think by himself before discovering already existing solutions, in order to facilitate the understanding.
[2003] A Static C++ Object-Oriented Programming (SCOOP) Paradigm Mixing Benefits of Traditional OOP and Generic Programming
In the Proceedings of the Workshop on Multiple Paradigm with OO Languages (MPOOL’03) Anaheim, CA, USA Oct. 2003
- Link at LRDE
- Abstract: Object-oriented and generic programming are both supported in C++. OOP provides high expressiveness whereas GP leads to more efficient programs by avoiding dynamic typing. This paper presents SCOOP, a new paradigm which enables both classical OO design and high performance in C++ by mixing OOP and GP. We show how classical and advanced OO features such as virtual methods, multiple inheritance, argument covariance, virtual types and multimethods can be implemented in a fully statically typed model, hence without run-time overhead.
[2002] Safe and efficient data types in C++ (Intègre)
LRDE technical report
- Link at LRDE
- Abstract: Using C++ builtin types is very unsafe as they are inherited from C types, which do not have overflow checking and have dangerous side effects and unexpected behaviors. Using intensive meta programming, it becomes possible to design safe data types with a minimal runtime overhead. As we want to be able to use existing algorithms, these types have to interact transparently with C++ builtin types. Primarily designed for Olena, a generic image processing library, our work needs to provide mechanisms to allow easy integration in generic algorithms.
Other
[2003] Theory of Evidence
LRDE technical report
- Link at LRDE
- Abstract: The theory of evidence, also called Dempster-Shafer theory or belief functions theory, has been introduced by Glenn Shafer in 1976 as a new approach for representing uncertainty. Nowadays, this formalism is considered as one of the most interesting alternatives to Bayesian networks and fuzzy sets. This report makes an overview of both theoretical and implementation aspects of this theory. After a short survey of the historical motivations for this theory, we present its interesting properties through the Transferable Belief Model formalism. From a more practical point of view, we propose a review of the existing optimizations for facing the #P complexity of Dempster-Shafer computations. This report introduces a new, promising concept to compute repeated fusions: the delayed mass valuation. Finally, we present Evidenz, our general-purpose C++ library for designing efficient Dempster-Shafer engines.
[2001] Neural Networks: Multi-Layer Perceptron and Hopfield Network
LRDE technical report
- Abstract: The ability of neural networks to derive meaning from complicated or imprecise data make them a powerful tool to extract hidden correlations between patterns or to recognize noised patterns. This report is dedicated to the study of Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLP) and Hopfield networks. In particular, two applications are detailed. MLP possibilities are illustrated through an image compression software and Hopfield networks are studied through a character recognizer. For both applications, theoretical principles, heuristic and algorithmic improvements are discussed thanks to various experiments.
PhD
Introduction
- Title: “A contrario statistical learning and efficient vision systems to detect meaningful visual events”
- Manuscript: PDF (fr)
We aim at proposing robust and efficient algorithms to detect meaningful visual events. Robustness implies, in particular, a close control of the number of false alarms made by an algorithm. Since the a contrario statistical approach has proved to match this concern, e.g. to detect geometrical primitives, we extend it to applications where the existing purely analytical framework is not adapted. By combining analytical computations with Monte-Carlo simulations or statistical learning, we applied a contrario reasoning to problems such as image segmentation into homogeneous regions, which rely on multiple features and on data-driven exploration heuristics whose mathematical properties are difficult to determine.
To satisfy the speed requirement, we also study efficient architectures. For low level vision, we experimented massive parallelism and developed a meaningful segments detection algorithm for programmable artificial retina, which operates in real-time. For high level tasks, we propose an agent-based and parallel architecture combining information priorization, parallelism between processing levels and top-down / bottom-up communications to implement “anytime” algorithms which provide results all along their execution, the most salient first. This architecture is applied to object matching and shows promising results.
Segment extraction
These principles were first applied to segment extraction in images using the computational power of the digital retinas developed at ENSTA by Thierry Bernard, resulting into an efficient, massively parallel, statistically-founded and parameterless algorithm (see acivs06).
A contrario image segmentation (acsegmentor)
The a contrario framework was then applied to a more complex problem, where exact computations are intractable: image segmentation into homogeneous regions. The resulting segmentation algorithm is called acsegmentor and can be used to filter out false alarms produced by existing algorithms. More details can be found on the project page.
Object matching
Finally, we worked on object detection within a parallel architecture (logical, not physical this time). The goal is to detect objects stored in a database (one picture per object) in new images. Thanks to a contrario learning, several similarity measures can be used in a statistically founded framework to increase detection rates. Accurate a contrario distributions can be learned with as few as 10 natural images which do not contain the database objects. Combined with an adapted, agent-based architecture, we show that this approach is suitable for an “anytime” implantation (see icvs08).